
Home About Us Core Strength News Products Case Services Contact Us
Publisher:Kagem Number of visits:349
With the development of advanced materials, resin letterpress and flexographic printing plates have also undergone many changes in the material, and it is no longer possible to distinguish the printing properties with a simple "resin plate". In the past, we often said that the resin plate and the washed plate represent the letterpress (Letterpress); the flexo and offset plates represent the Flexography. However, at present, the relief material can be softly applied to the flexographic printing machine, and the flexo can be applied to the letterpress printing machine, and the flexo is also a type of letterpress, and is also called an elastic relief in Taiwan.
After the dispute over the above nouns, we have temporarily summarized the plate and printing methods as a simple conclusion to reduce some unnecessary synonymous between the industries:
1 embossing, using a letterpress.
2 flexo, use flexo.
Now we try to discuss the classification, imaging principle, plate making process and the techniques in actual production in a more complete way. In the process, some flexographic data is added as a reference comparison. Part of this article is based on the principle of flexographic imaging written by the plate company and the previous one. In addition, some production techniques have been added for the production of the letterpress.
First, the classification of the letterpress
The application of the letterpress is very broad: rotary (half-rotation) printing, flat (flat flat) printing, dry offset printing, blanching, stamping, pad printing and so on. Common well-known brands include: Flint, TOYOBO, BONPOLY, and TARAY. For all kinds of different applications, there will be some differences in the plates used. The commonly used plates are divided into the following types (see Figure 1):
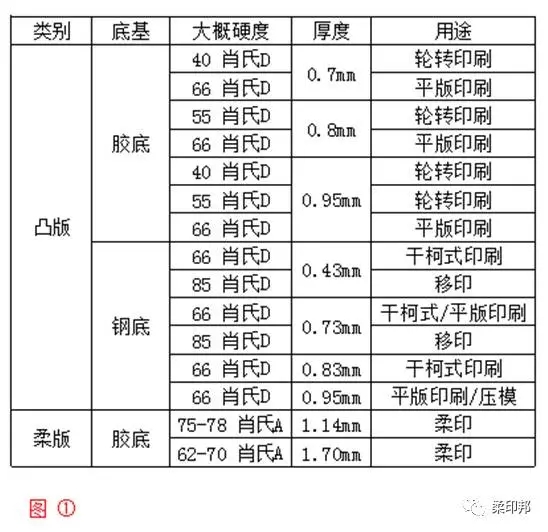
In addition, due to different imaging principles, the letterpress is further divided into: 1 digital laser imaging letterpress; 2 traditional film imaging letterpress.
Due to the difference of the display liquid, it is further divided into: 1 water washing (water development); 2 alcohol washing (alcohol development). However, the general application products currently on the market are mainly washed with water.
As for the differences in raw material components such as nylon and PVA between different brands, no distinction will be made here.
Second, the principle of letterpress imaging
1. The plate structure of the letterpress
The principle of the letterpress is similar to that of the flexo, which is formed by curing the photosensitive material under the action of ultraviolet rays.
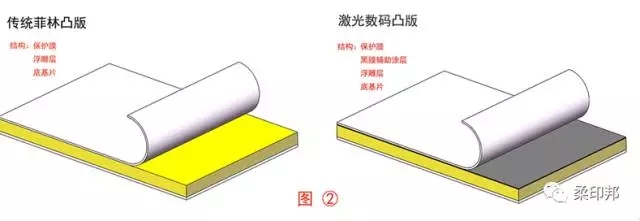
As can be seen from Figure 2, the difference between the conventional sunscreen image relief and the digital laser relief is the auxiliary coating and the black coating.
1) The embossed layer of the traditional film embossed plate has a lightly frosted surface shape, which is beneficial to the air between the film and the plate by vacuuming after the film is applied to the film, thereby achieving a better sticker. Hehe.
2) The black coating of the digital laser plate replaces the film and directly burns the image by laser. Because there is no need for a vacuum process such as film, the black coating is smooth. The desired content pattern is burned directly on the black coating.
In addition, for the base portion of the relief, as shown in the table of Fig. 1, there is a distinction between the rubber base and the steel base.
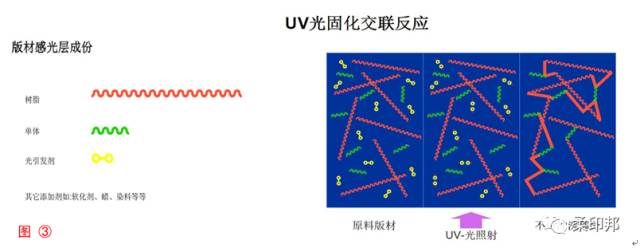
2. Composition and principle of the photosensitive layer of the plate
From Figure 3 (provided by Flint), we can see the composition of the plate. The resin is the most important material for the relief photosensitive layer. The photoinitiator cross-links the resin and the resin by absorbing UV rays. The image portion of the ultraviolet light will become solid. The portion that is not irradiated with UV (the portion that is blocked by the film of the film or the black film of the laser version) is still a soft uncured resin, and this soft resin will dissolve during the plate washing. The right side of Figure 3 is a schematic representation of the crosslinking reaction. After recognizing these principles, you can understand the method of setting production parameters mentioned in the following article.
Third, RIP electronic color separation and imaging
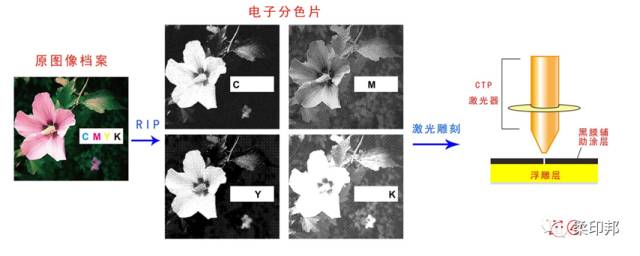
Before printing, we need to translate the designer's infinite creativity into four colors or a limited number of colors to express the design idea. The printed pattern is calculated by the RIP software algorithm to generate a 1-Bit-TIF image file, for example, four files of CMYK four colors, and four colors simulate the original pattern effect by superposition, gray scale, and the like. Then, the four 1-Bit-TIF files are outputted through the imagesetter, or the graphics of the TIF file are directly engraved on the digital laser flexo by the CTP machine, as shown in Fig. 4.
Fourth, the plate making process
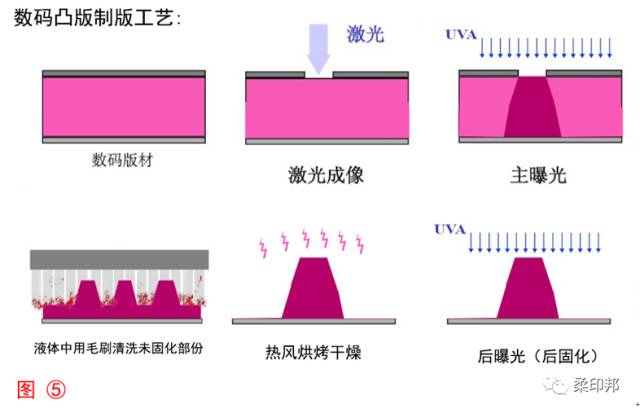
After understanding the structure and composition of the plate, combined with RIP color separation and imaging principles, we can easily understand the production process using Figure 5 as a whole. Because the share of film making has become less and less, and because it is not environmentally friendly and unstable, it has been basically stopped in many developed countries. Therefore, we focus on the laser plate making process. If we use film making, we can understand the top layer of black coating as film, and the laser burning image is the light-transmitting part of the film.
The sequence of the process of letterpress production is: plate laser imaging → main exposure (exposure imaging) → washing → drying → post exposure.
Detailed description of the project:
1. Laser imaging: The laser burns out the black coating on the black coating. The black coating above the required image is burned off, allowing the UV light to pass through and enter the photosensitive resin layer for cross-linking reaction.
2. Main exposure (exposure imaging): The ultraviolet light enters the photosensitive resin layer through the notch of the burnt black coating, and the portion irradiated with ultraviolet rays is solidified after the crosslinking reaction, and the portion blocked by the black coating is ultraviolet rays. Still in a state of not being cured.
3. Washing: After the required content has been completed and the crosslinking reaction is cured, the resin plate is placed in a washing machine for washing, and the semi-fluid resin which has not been solidified is dissolved. Here, the different plates are roughly divided into pure water washing and alcohol washing (pure water is added to a specific proportion of alcohol)
4. Drying: After the plate is washed, the solution will remain on the surface of the plate, and some will enter the inside of the resin to make the plate expand. We need to dry the plate to evaporate and dry the solution on the surface. And evaporate the solution into the interior and return to the plate within 103% of the thickness before cleaning.
5. Post-exposure: After all the above steps were completed, the plate was subjected to an overall photo-curing with UVA. For example, in the main exposure, the underlying resin of the black coating is not cured, and the final post-exposure is used to completely crosslink the position of the intermediate layer including the material to make the life longer.
5. Selection and testing of plate making equipment
1. Why choose laser plate making equipment and give up the traditional film making.
In the age of digital digital, whether to choose digital plate making is not a topic worth discussing. At present, the most commonly used laser engraving machines in the Chinese market are the Speak series made by ESKO (Isco) and the Chinese Amsky (2013). The AURA series was launched in the year.
A detailed understanding of the differences between laser plate making and film making is conducive to understanding the inevitability of developing laser digital plate making technology.
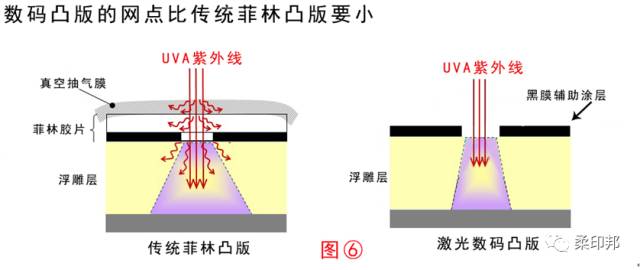
The scattering of the light from the printing plate in Fig. 6 can be more clearly understood, why the digital plate making is more refined than the conventional film making, and thus the image difference of FIG. 7 is greatly different.
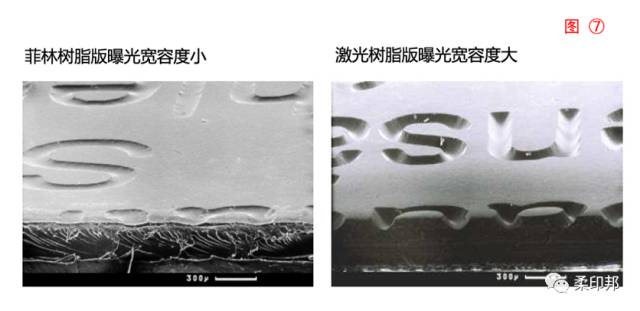
The biggest advantage of digital plate making is not only that it can image fine dots, but its low scattering, which makes the printing plate more tolerant, even tolerant to small reverse white and 1% fine dots. Imaging is achieved without the need for partial occlusion of the mask. As long as your printer configuration is relatively standard, regardless of the content difference of the same plate, we only need to set the same plate time, that is, to achieve zero technical.
2. How big is the size of the printer and the lamp power?
The true effective area of the plate-making machine is not the same as the size of the table. The effective area of the plate-printing size is not as intuitive as the plate-washing. It can be done by observing whether it can be washed at the same time. If the energy of the printing machine is not balanced, the labeling points of each die will be different.
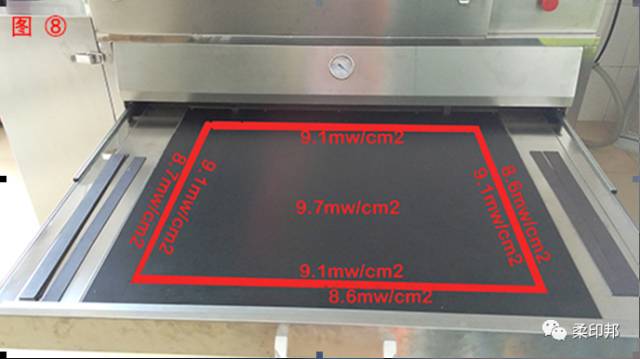
As shown in Fig. 8, after passing the UV intensity meter measurement, we select the red-frame area with more balanced energy as the printing position and mark it to ensure that the stable area is not exceeded during production.
To understand the cause of this problem, we need to understand the arrangement and structure of the lamp.
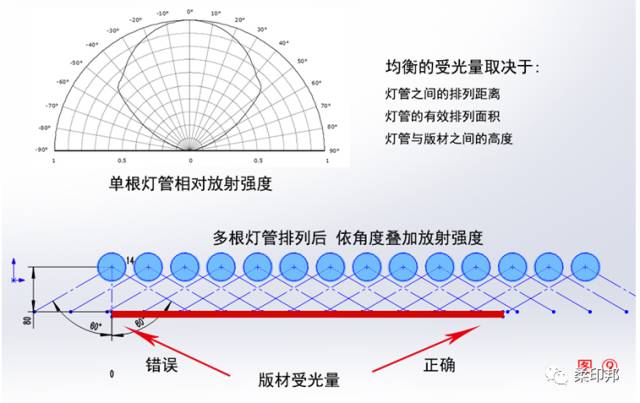
As shown in Fig. 9, the cylindrical type of tube has a very large difference in ultraviolet radiation intensity at different angles, and the ultraviolet intensity at the 0 degree position directly below the tube is the highest. In addition, when the lamps are arranged, the sum of the ultraviolet rays of the drying table is the superposition of the radiation values of the plurality of lamps at different distances and angles. It can be seen from Fig. 9 that the different positions of the plate under the lamp tube will be affected by the radiation values of the lamps of different strengths, and the difference in the total amount of ultraviolet rays absorbed will make the flat net uneven. To do this, we must ensure that the position of the plate is placed at the same time below the third lamp on the left/right side of the side-by-side lamp. In the conventional 60w lamp, like the plate placement method of Figure 9, the UV intensity on the left side of the plate may be 6mw/cm2, and the UV intensity on the right side of the plate may be 9mw/cm2. There are differences between the two models, which will definitely affect the printing effect.

In addition to the width of the tubes side by side, the actual effective length of the tube will also affect the quality of the plate. As shown in Fig. 10, the total length A of the lamp includes the lamp cap and the filament, and the positional energy of the filament is very low, and even the outermost ends of the lamp have no ultraviolet radiation value. In actual test, we get a lamp of various powers, and the actual effective length that meets the requirements of the printing plate is the B value. From this data, it can be found that the 40W lamp can be considered not suitable for such plate making. It is recommended that you choose a 60W lamp when purchasing the device.
In addition, it can be seen from the luminous intensity in the upper left corner of Fig. 10 that there is a difference in the radiation intensity between the left and right ends of the lamp tube. In order to make the energy of the printing plate more uniform, we need to alternately install the end of the lamp with the word and the end without the word.
3. Effective area and maintenance of the plate washer
The effect of the plate washer is relatively straightforward. Most of the plate washers on the market are designed to be simple and used for many years, and the appearance between different brands is very similar. However, the rotary plate washer needs some maintenance and parameter adjustment after using it for some time. As shown in (Fig. 11), this is a modified version of the large-format washing machine. Its appearance is close to that of the machine on the market. The structure of the plate washer is designed to rotate the upper brush and the lower plate is fixed. To facilitate the pasting of large areas of the plate. The conventional structure on the market is that the top plate is rotated and the lower brush is fixed.
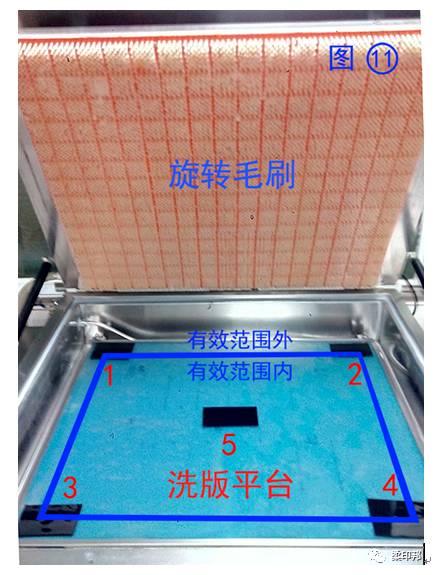
1 The effective range of the plate washing platform.
For machines with the same size as the size of the platen platform, the effective area of the platen platform must be reduced by the radius of rotation of the brush (or the radius of rotation of the platen), otherwise the edge of the platen platform is equal. During the plate-washing time, the friction time is reduced by half. The blue area of the frame (Figure 11) is the effective area of the plate.
2 Four orientations of the washing platform are adjusted.
After the plate washer has been applied for a period of time, due to the rotary movement of the platform, the adjusting screws of the four corners of the platform or the brush may be loosened. Or sometimes the operator does not have a fixing screw for fixing the brush in order to facilitate the cleaning of the brush. Therefore, it is necessary to place some small-area test plates (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 in Figure 11) at the four corners and the middle of the platform after each use of the plate washer for a period of time. At most, wash for 30 seconds - 60 seconds - 90 seconds - 120 seconds to observe the dissolution of 5 small plates. When it is found that a certain sheet dissolves at a particularly slow rate, it is possible that the platform in this orientation is lower, and the fixing screws need to be adjusted to maintain the balance of the frictional pressure of the platform.
4. How high the dpi resolution is required for the laser letterpress/flexographic CTP engraving machine.
In the circular laser spot engraving system, our common laser imaging system resolution is 2540dpi, 4000dpi, 5080dpi, and even more advertised as 9600dpi. In fact, what is the resolution we need for conventional printing? Is the higher the better?
1) Consider the need for high-definition printing for laser imaging resolution from the perspective of electronic document imaging. Although the recognition rate of the human eye in the 0%-100% grayscale gradient is about 110, the electronic file file system divides the grayscale into 256 levels. In addition, the current maximum number of imaging lines for flexo and letterpress is 175Lpi to 200Lpi (to retain 1% of the dots and sacrifice 96% for the Internet). Then use this data to calculate the resolution requirements for high-definition printing: 2800dpi for 175Lpi and 3200dpi for 200Lpi.
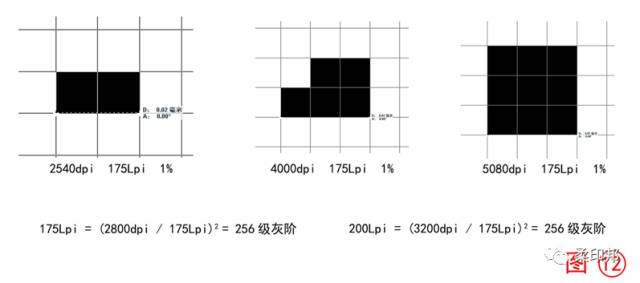
At the same time, as can be seen from Figure (12), the same 175Lpi 1% dot shape is different at different resolutions, but the maximum diameter is the same. In practical applications, it is common to use a 2540dpi machine to engrave and image a 175Lpi dot, but the laser CTP uses a mild aging after 1 to 2 years, making the small dots unstable.
2. The need for laser imaging resolution is considered in terms of production efficiency. For every doubling of the file resolution, the file size will increase by a factor of three (Figure (13)). Under the increasingly complex and exquisite concept of printed archives, today's archives are very large. File access and computing are also very demanding on computer computers. If we use high resolution without purpose, it will be at the expense of productivity. The finished product obtained does not increase in proportion.

In addition, from the shape of the dot of the figure (12), we can also calculate that the laser resolution increases, and in the case of the same number of laser beams, the speed of engraving imaging is proportionally decreased, and the production time will be longer.
3. Consider the need for laser imaging resolution from optical imaging effects. Flexo is an elastomeric imaging material with large fluctuations in thickness. There is a margin of error for each thickness, and fluctuations within 5% are also present in mature large brand suppliers. For example, the 1.14mm version will show 1.18mm, which is quite different from the offset of the offset PS plate. At the same time, the laser spot will become shallower as the resolution increases, and the spot will be shallower and shallower. If the depth range of the deep depth cannot be achieved, when the thickness of the plate changes, or if there is dust at the bottom of the plate and the distance between the plate and the laser lens is changed, the out-of-focus phenomenon may occur, causing the engraving to be unclean.
At present, the technology of nominal high resolution is also a virtual upgrade of optical resolution through soft plug-in operations.
In addition, in practical applications, the development engineer will also set the highest recognition grayscale of the human eye to 200, and use the 2800dpi engraving 200-line printing plate, which can also meet the requirements of production efficiency and human eye recognition. However, current conventional devices do not have a 2800dpi configuration.
Combining the current market conditions of flexo and embossing, considering the practicality and stability considerations, the optical resolution of 4000dpi will be an ideal choice.
Six, common parameters of plate making and actual production skills
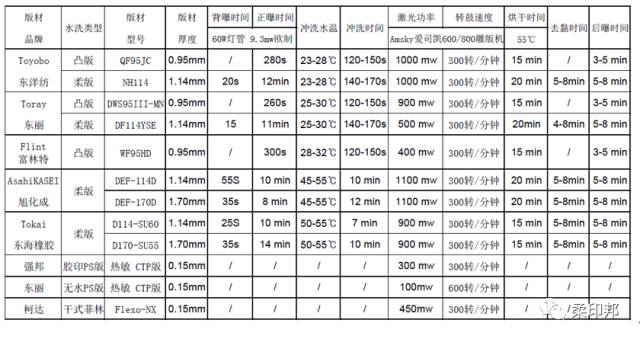
1. Platemaking parameters of common plates.
For ease of reference by the plate makers, the production parameters are now listed for reference in accordance with the most stable use of the letterpress type and plate making equipment on the market, and some washable flexo sheets are listed for comparison with companies that use both printing technologies. However, each company should make appropriate adjustments and optimizations according to the year of use and actual conditions of its equipment.
2. Actual production techniques in letterpress production.
For the letterpress production process, we often clean directly after the main exposure. However, for some anti-counterfeiting dotted lines or particularly small characters composed of dots, the resulting version of the scrap is very high, and the outlets are prone to defects.

As shown in Figure (14), this type of line is often seen on the drug label and other products. To make the effect of the letterpress, we can turn over the plate first, and then do the back exposure for 2-5 seconds. This effect: 1. Let the relief produce a very thin base, and the dots are stronger. 2. It is not easy to dissolve the bottom of the dot during the plate cleaning after the base is cured. Although this method produces a little foundation, it does not affect the use of printing, in actual use or in seconds.
3. How to adapt to the transition from film making to laser plate making faster.
Laser plate making further reduces the requirements for plate makers and makes production more stable. However, in terms of the effect of printed products, the early stages of use often lead to the detour of the plate making department and the design department. The main reason is that the differences between the laser plate making outlets and the film making outlets are not properly understood, and the plate makers are forced to return to experience. Set the old road for the printing time. The most common problem is to directly call the previous version of the Philippine version of the file to produce the laser version, but can not achieve the original gradual transition effect, the new laser version of the transition effect edge is too hard, so that the print version staff deliberately reduce the exposure time to make small outlets Dissolved, so dead loops that laser platemaking technology cannot be used. This problem also applies to the production and printing of flexo.
To understand this reason, we need to correctly understand the difference between film outlets and laser dot molding.
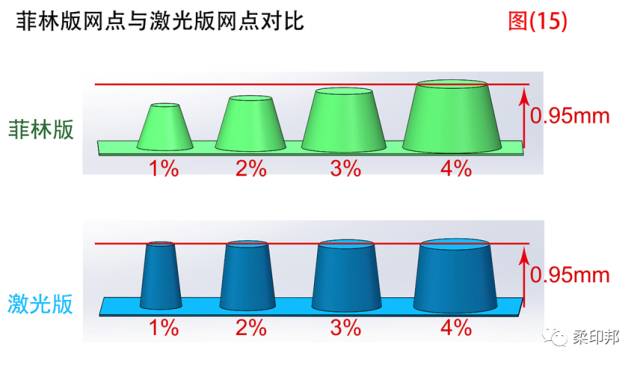
It can be seen from Figure (15) that 1%-3% of the 175Lpi small dots in the film making process are shorter than the normal dots, and there will be a slight slight ink on the printing pressure, and a gradient transition effect such as the printed sun circle. More balanced, less edge ink and more acceptable. In laser plate making, the height is the same from all the dots of 1%-4%, so the high-gloss effect edges printed on all the dots can be thicker.
At the same time, it can be observed that the laser dot is more vertical and finer. In this case, we should make reasonable use of the characteristics of the laser version, and more use pre-press design techniques, such as paving a 1% dot in the high-gloss net position to avoid the break, without worrying that the small dot can not be formed.
Therefore, the original Sunfeilin file and the laser version of the file cannot be directly used by each other. Prepress personnel should concentrate on understanding the principle of laser plate making and adapt to the device more quickly. In the initial stage of using the laser plate-making machine, you can do some test charts including yin and yang characters, yin and yang lines, gradient circles, etc., and use the laser version and the film version to compare the effects of the two, and adjust the direction of the design according to their respective characteristics.
This article is reproduced in the "Soft Printing State" WeChat public number. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete.

Guangdong Jiajing Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Kagem), founded in 1999, specializes in the R&D, production and sales of water-based inks, water-based varnishes, water-based acrylic resins, water-based acrylic emulsions, pearlescent binders and other eco-friendly water-based printing materials.
Add: Shibu Industrial Zone, Liaobu Town,Dongguan, Guangdong 523000 CHINA
Main Line:0086-769-82318231
Fax:0086-769-82318555
Sales:0086-769-82318668
Fax:0086-769-82311109
E-mail:sales@kagem.net